Optimizing Interconnect vs. VPN: Latency, Throughput, and Real-World Use Cases on Google Cloud
As organizations modernize their infrastructure, migrating from traditional datacenters to cloud-native platforms, network connectivity becomes a central architectural decision. And on Google Cloud, one of the most common debates among experienced leaders is:
Should we use Interconnect or VPN to connect our on-prem or WAN to the cloud?
This isn’t a simple pricing comparison. It’s a decision that impacts:
- Latency
- Throughput
- Reliability
- Security
- Hybrid workloads
- Disaster recovery
- Data transfer strategies
- Future scalability
If your business runs mission-critical systems, builds multi-region architectures, or supports global customers, choosing the right connection method directly affects performance, downtime risk, and operational experience.
Let’s break this down deeply and practically.
1. Setting the Stage: Why Connectivity Matters More Today
In the early cloud days, enterprises used VPN primarily as a secure tunnel from on-prem to cloud. It was simple, inexpensive, and enough for low-traffic workloads.
But as cloud adoption matured, businesses started pushing far more demanding requirements:
- High-throughput data pipelines
- Latency-sensitive applications
- Real-time analytics
- Distributed microservices
- Hybrid database replication
- Cross-region failover
- Global service architectures
At this stage, VPN suddenly becomes a bottleneck.
This is where Interconnect—Google’s private, high-speed connection—enters the story.
But choosing between the two depends not only on speed, but also your business model, your workloads, and your long-term roadmap.
2. A Clear Breakdown: What Is VPN vs. What Is Interconnect?
Before diving into architecture decisions, let’s define them side-by-side.
What Is a Google Cloud VPN?
A secure IPSec tunnel that connects your on-prem/branch to Google Cloud.
- Uses the public internet
- Encrypted tunnel through IPSec
- Quick to configure
- Low to moderate throughput
- Moderate latency (depends on internet routing)
- Highly cost-effective
GCP offers:
- Classic VPN
- HA VPN (High Availability VPN with SLA-backed reliability)

What Is Google Cloud Interconnect?
A high-bandwidth, private physical connection between your network and Google.
Two types:
1. Dedicated Interconnect
A physical port directly into Google’s edge, offering:
- 10 Gbps or 100 Gbps per link
- Up to 200 Gbps aggregate per VLAN
- Lowest latency possible
2. Partner Interconnect
Connectivity via a Google Cloud partner:
- More flexible bandwidth options (50 Mbps to 50 Gbps)
- Easier provisioning
- Suitable for remote/global locations
Interconnect doesn’t send traffic over the public internet—it uses Google’s private backbone.
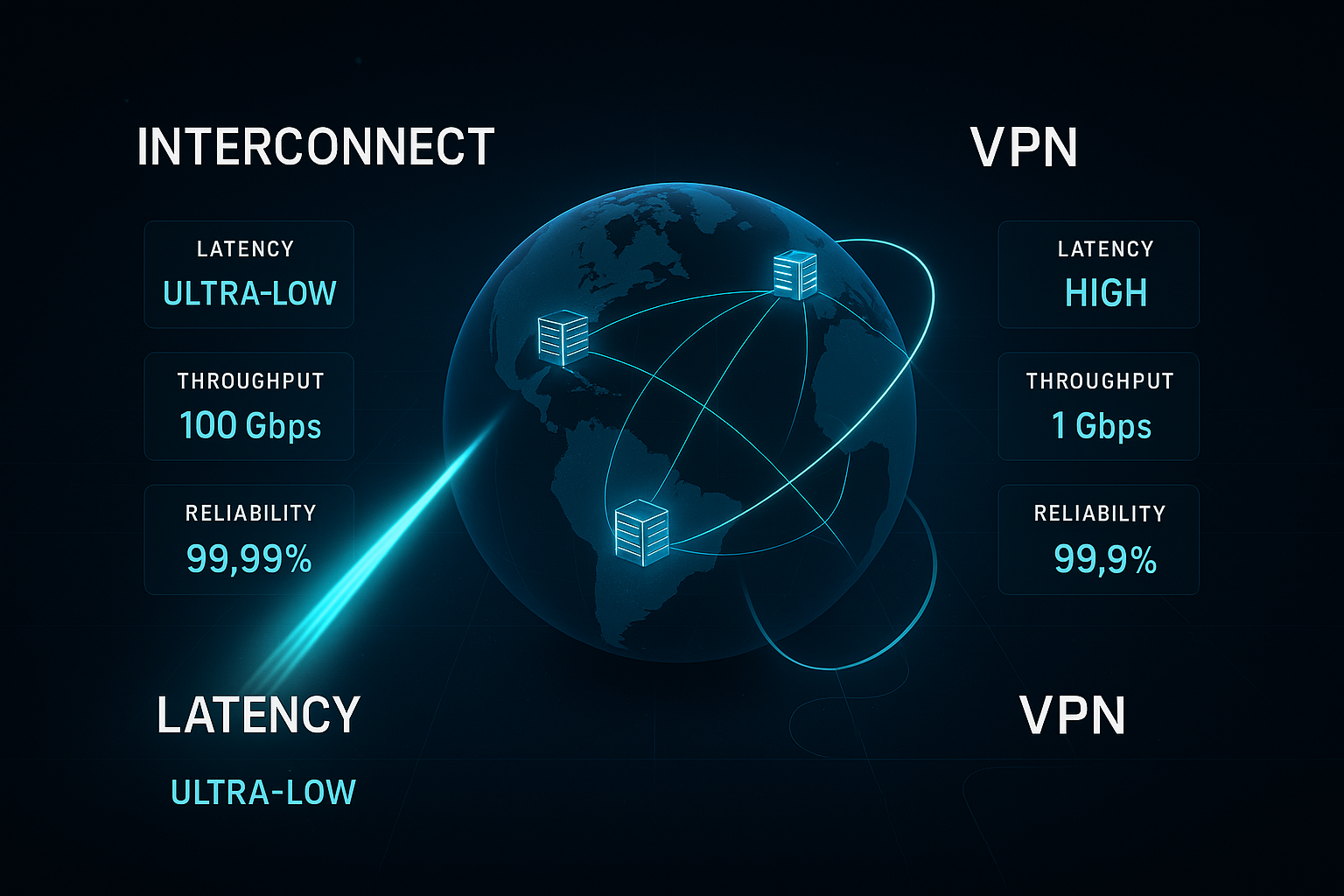
3. Latency: How Much Does It Really Matter?
Latency isn’t only a number—it’s a business outcome.
For some businesses, shaving 20–30 milliseconds doesn’t matter.
For others, it changes everything.
Let’s compare.
VPN Latency
- Travels over public internet
- Variable based on ISP routing
- Unpredictable during congestion
- Latency spikes during peak hours
- Higher jitter
Real-world ranges: 30–150 ms, depending on geography.
VPN latency is rarely stable because you don’t control the network path.
Interconnect Latency
- Traffic enters Google’s network as early as possible
- Google’s private backbone carries it end-to-end
- Predictable, low-jitter connectivity
Real-world ranges: 2–20 ms between your datacenter and Google’s PoPs.
Mission-critical latency matters when you’re running:
- Live bidding platforms
- Video streaming platforms
- Financial trading systems
- Real-time gaming
- Hybrid transactional databases
- Global microservices
If latency changes your performance metrics or customer experience, Interconnect is the solution.
4. Throughput: The Real Bottleneck in Hybrid Architectures
Throughput determines how much data you can move—and how fast.
VPN Throughput
VPN is constrained by:
- IPSec processing overhead
- Internet throughput limits
- Single-tunnel bandwidth limitations
HA VPN improves reliability, but throughput still tops out at:
- ~3–10 Gbps (multiple tunnels)
- Often less in real-world conditions
Sufficient for:
- Control-plane traffic
- Occasional data transfers
- Small-to-medium workloads
Not suitable for:
- Terabyte-scale analytics pipelines
- BigQuery batch transfers
- Hybrid storage syncing
- High-volume backups
- ML data ingestion
- Massive replication streams
Interconnect Throughput
Dedicated Interconnect offers:
- 10 Gbps or 100 Gbps per link
- LAG (link aggregation) for scaling
- Partner Interconnect offering 50 Mbps → 50+ Gbps options
In high-throughput architectures, Interconnect becomes critical:
- Multi-terabyte daily ETL
- Streaming data into Pub/Sub
- BigQuery ingestion from datacenter
- Hybrid applications like SAP
- Active/Active multi-region deployments
- High-volume media content movement
Interconnect isn’t just faster—it makes large-scale architectures operationally feasible.
5. Reliability and SLAs: Where the Business Case Gets Stronger
VPN Reliability
VPN depends on:
- Internet routing stability
- ISP reliability
- Tunnel failovers
- Cloud router BGP stability
HA VPN significantly improves uptime with:
- 99.99% SLA
- Automatic failover tunnels
- Dual gateways
But VPN is still subject to the public internet’s unpredictability.
Interconnect Reliability
Dedicated Interconnect offers:
- 99.9% to 99.99% SLAs depending on redundancy
- Dual-homed connections (Highly Recommended)
- Private, deterministic routing
- Stable throughput
- Better failover consistency
When your network cannot go down, Interconnect wins by a wide margin.
6. Security: Both Are Secure, but Not Equal
VPN Security
- IPSec encrypted
- Traverses public internet
- Requires strong key rotation and policies
- Vulnerable to ISP outages or routing issues
Ideal for secure tunnels, but not ideal for highly sensitive workloads.
Interconnect Security
- Private physical connection
- Never traverses public internet
- Data flows into Google’s private backbone
- Integrates seamlessly with VPC Service Controls
- Lower attack surface
For regulated industries—finance, healthcare, telecom—Interconnect simplifies compliance.
7. Cost Considerations: It’s Not About Price Alone
Cost is a major factor, but the decision shouldn’t be based purely on price.
VPN Costs
Very low.
Typically:
- Per-hour pricing for cloud VPN gateways
- Minimal data transfer fees
Best for small teams, development workloads, or low-throughput apps.
Interconnect Costs
Higher upfront, but not always expensive long-term.
Costs include:
- Port fees
- Cross-connect fees (at colocation site)
- Data transfer (lower than internet egress)
- Provisioning or partner cost (for Partner Interconnect)
But Interconnect often reduces egress costs compared to public internet pricing.
For companies moving petabytes annually, Interconnect is often cheaper than VPN.
8. Real-World Use Cases: When to Use VPN vs Interconnect
You can’t choose correctly without looking at practical scenarios.
When VPN is the Better Choice
1. Small or early-stage deployments
Proof of concept
Development environments
Light workloads
2. Remote offices or branch connections
Low bandwidth
Event-driven workloads
User authentication traffic
3. Backups and administrative connections
Monitoring
Control-plane operations
Occasional data movement
If cost is the biggest concern and performance isn’t critical—VPN works.
When Interconnect is the Better Choice
1. High-throughput hybrid workloads
You need consistent bandwidth for:
- ETL jobs
- Data lake ingestion
- ML model training
- Media encoding
2. Latency-sensitive architectures
Such as:
- Distributed microservices
- Game servers
- Financial trading systems
3. Hybrid transactional databases
For example:
- On-prem Oracle <-> GCP
- Cloud SQL read replicas
- Spanner multi-region sync pipelines
4. Compliance or regulatory requirements
Interconnect simplifies:
- PCI
- HIPAA
- FFIEC
- Banking regulations
5. Large enterprises with strict SLAs
If uptime is contractual, Interconnect gives control and predictability.
9. Combining Both: The Best of Both Worlds
Many mature organizations use both Interconnect and VPN.
Typical pattern:
- Interconnect as the primary path (high speed, low latency)
- HA VPN as backup failover
- Cloud Router handles BGP-based routing decisions
- Traffic switches automatically
This creates a hybrid network with:
- Redundancy
- High throughput
- Reliable failover
- Lower latency
- No single points of failure
This is the architecture recommended for mission-critical workloads.
10. Making the Decision: A Simple Framework for Leaders
To choose the right connectivity method, ask:
A. What is your required throughput?
< 5 Gbps → VPN may be fine
5 Gbps → Interconnect recommended
20 Gbps → Interconnect required
100 Gbps → Dedicated Interconnect only
B. How sensitive are you to latency?
Latency-critical workloads always prefer Interconnect.
C. How much data will move between on-prem and GCP?
Petabyte-scale = Interconnect
Moderate or unpredictable = Possibly VPN + caching
D. Do you have compliance obligations?
Private connectivity often simplifies audits.
E. How mature is your cloud environment?
Proof of concept → VPN
Enterprise migration → Interconnect
Two-way hybrid architecture → Interconnect + VPN failover
Final Thoughts
Choosing between Interconnect and VPN isn’t just a networking choice—it’s a strategic infrastructure decision that shapes your cloud architecture, performance, and operational resilience.
VPN is flexible, quick, inexpensive, and perfect for low-volume or development scenarios.
Interconnect is built for speed, low latency, reliability, and high-throughput hybrid architectures.
For modern enterprises aiming for predictable performance, strong SLAs, and future scalability, Interconnect becomes the clear backbone. And when combined with HA VPN for redundancy, it forms a rock-solid connectivity strategy that supports mission-critical workloads on Google Cloud.
Recent Posts
- Building a High-Performance VPN Mesh for Distributed Teams
- Building Resilient VPN Architectures Using Route-Based VPN and Tunnel Interfaces
- Understanding SonicWall DPI-SSL Architecture and Its Impact on Throughput
- Advanced Threat Prevention: Inline ML and DNS Security Architecture Explained
- App-ID: How Palo Alto Firewalls Identify Traffic Beyond Ports & Protocols
Recent Comments
- ISO 27001 Certification Audit on The Impact of Quantum Computing on Cybersecurity: Preparing for the Future
- ISO 27001 Certification Audit on The Impact of Quantum Computing on Cybersecurity: Preparing for the Future
